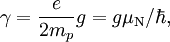Gyromagnetic ratio
From NMR Wiki
The formula is:
where μN is the nuclear magneton, and g is the g-factor of the nucleon or nucleus in question.
The gyromagnetic ratio of a nucleus is particularly important because of the role it plays in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). These procedures rely on the fact that nuclear spins precess in a magnetic field at a rate called the Larmor frequency, which is simply the product of the gyromagnetic ratio with the magnetic field strength.
Approximate values for some common nuclei are given in the Table below.<ref>Template:Cite book</ref>
| Nucleus | γ / 2π (MHz/T) |
|---|---|
| 1H | 42.576 |
| 3He | -32.434 |
| 7Li | 16.546 |
| 13C | 10.705 |
| 14N | 3.0766 |
| 15N | -4.3156 |
| 17O | -5.7716 |
| 23Na | 11.262 |
| 31P | 17.235 |
| 129Xe | -11.777 |