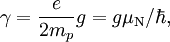Gyromagnetic Ratio
From NMR Wiki
Gyromagnetic Ratio is defined by:
where 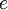 is the magnitude of electron charge,
is the magnitude of electron charge, 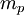 is the proton mass,
is the proton mass, 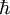 is reduced Planck constant,
is reduced Planck constant, 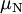 is the nuclear magneton, and
is the nuclear magneton, and 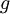 is the g-factor of the nucleon or nucleus in question.
is the g-factor of the nucleon or nucleus in question.
Approximate values for some common nuclei are given in the Table below.<ref>Template:Cite book</ref>
| species | γ / 2π (MHz/T) [1] | |
|---|---|---|
| free electron | 2.80249536 x 104 [2] | |
| 1H | 42.576 | |
| 2D | 6.53593 | |
| 3He | -32.434 | |
| 7Li | 16.546 | |
| 13C | 10.705 | |
| 14N | 3.0766 | |
| 15N | -4.3156 | |
| 17O | -5.7716 | |
| 19F | 40.0593 | |
| 23Na | 11.262 | |
| 31P | 17.235 | |
| 75As | 7.2919 | |
| 129Xe | -11.777 |
For information on individual chemical elements please use NMR and EPR Periodic Table
To find NMR frequency of your favorite nucleus at a given magnetic field, see Alex Jerschow's on-line Interactive NMR Frequency Map
References
- values are divided by 2*pi, those in nist tables are not
- gyromagnetic ratio of free electron