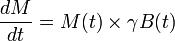Bloch equations
From NMR Wiki
(Redirected from Bloch equation)
Bloch equation describes evolution of classical magnetic moment in the magnetic field. The equation in the absence of T1 and T2 relaxation is:
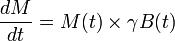
Summary explanation
A particle with a magnetic moment M in the magnetic field B will experience change of its mechanical angular moment J, i.e. torque = dJ/dt.
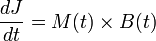
Wigner-Eckart theorem in quantum mechanics proves that particle's magnetic moment is collinear with it's angular moment so that:
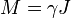 ,
,
where γ is the scalar quantity called gyromagnetic ratio of the particle.
Therefore we have expression (known as Bloch Equation):