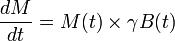Bloch equations
From NMR Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | Bloch equation describes evolution of classical magnetic moment in the magnetic field. | + | Bloch equation describes evolution of classical magnetic moment in the magnetic field. The equation is: |
| + | <math>\frac{dM}{dt} = M(t) \times \gamma B(t)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Summary explanation== | ||
A particle with a magnetic moment '''M''' in the magnetic field '''B''' will | A particle with a magnetic moment '''M''' in the magnetic field '''B''' will | ||
experience change of its mechanical angular moment '''J''', i.e. torque = dJ/dt. | experience change of its mechanical angular moment '''J''', i.e. torque = dJ/dt. | ||
Revision as of 01:24, 7 July 2009
Bloch equation describes evolution of classical magnetic moment in the magnetic field. The equation is:
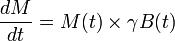
Summary explanation
A particle with a magnetic moment M in the magnetic field B will experience change of its mechanical angular moment J, i.e. torque = dJ/dt.
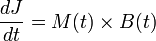
Wigner-Eckart theorem in quantum mechanics proves that particle's magnetic moment is collinear with it's angular moment so that:
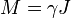 ,
,
where γ is the scalar quantity called gyromagnetic ratio of the particle.
Therefore we have expression (known as Bloch Equation):