SCUBA
From NMR Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
m |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''SCUBA''' - '''s'''timulated '''c'''ross peak '''u'''nder '''b'''leached '''a'''lphas. | '''SCUBA''' - '''s'''timulated '''c'''ross peak '''u'''nder '''b'''leached '''a'''lphas. | ||
| - | <pulse> | + | <pulse title="scuba pulse sequence element for water suppression retaining H alpha resonances"> |
anchors: @a @b @c,d,e @f @g | anchors: @a @b @c,d,e @f @g | ||
disp: 5@a 5@b 10@d 10@f 5@g | disp: 5@a 5@b 10@d 10@f 5@g | ||
Revision as of 00:40, 14 February 2009
SCUBA - stimulated cross peak under bleached alphas.
SCUBA[1] is a method of water suppression applicable for macromolecules that avoids a problem of bleaching signals that overlap with water resonance (such as Hα protons in the proteins).
Method works for systems where T2 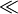 T1. A value of 60 ms was used for human ubiquitin at 500 MHz.
T1. A value of 60 ms was used for human ubiquitin at 500 MHz.
Figure above illustrates preparation sequence incorporating SCUBA element. Delay τ must be < T1.
References
- BROWN, SC and WEBER, PL and MUELLER, L. Toward complete 1H NMR spectra in proteins. Journal of magnetic resonance 77(1):166--169, 1988. BibTeX

