Analysis of HETLOC data
From NMR Wiki
First, list couplings that need to be collected (chances are all observable couplings won't be needed).
HETLOC experiment has a limitation that it won't show couplings to carbon atoms (or other X-nuclei) if they are not connected to a proton.
Then, for a given coupling between atoms Cx and Hy:
- draw a horizontal line at ω1 (usually y-dimension) = δ Hx - i.e. chemical shift of Cx-attached proton.
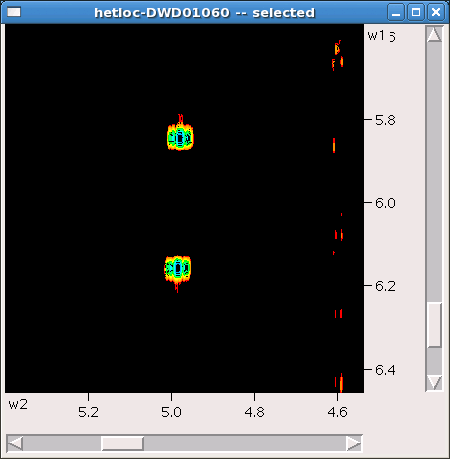
Zoom onto the peak of interest (see below). As you can see the peak is split in w1 by one bond CH coupling. Also there is a slight shift of one component with respect to another in w1 - amount of that splitting in Hz equals remote JCH we are looking for.
Read frequencies of the two peaks as described here and substract position of one peak in Hz along w2 axis from position of another.